What is Gout?
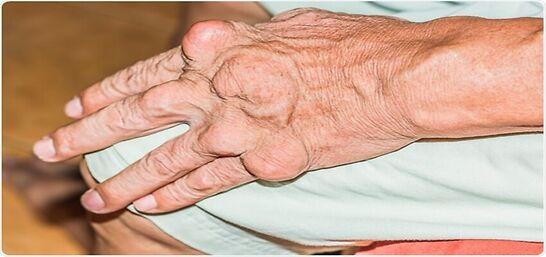
Gout is a form of arthritis characterised by severe pain, redness and tenderness in joints.
An attack of gout can occur suddenly, often waking you up in the middle of the night with the sensation that your big toe is on fire.
What are the signs and symptoms of Gout?
It's characterized by sudden, severe attacks of pain, swelling, redness and tenderness in one or more joints, most often in the big toe.
The possible signs that may help you out are:
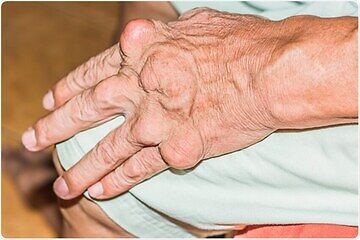
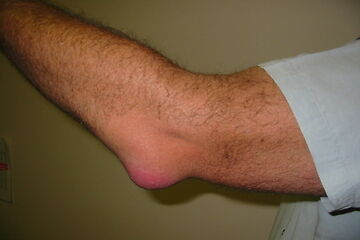
- Intense joint pain. Gout usually affects the big toe, but it can occur in any joint. Other commonly affected joints include the ankles, knees, elbows, wrists and fingers. The pain is likely to be most severe within the first four to 12 hours after it begins.
- Lingering discomfort. After the most severe pain subsides, some joint discomfort may last from a few days to a few weeks. Later attacks are likely to last longer and affect more joints.
- Inflammation and redness. The affected joint or joints become swollen, tender, warm and red.
- Limited range of motion. As gout progresses, you may not be able to move your joints normally.
Immediately contact your doctor if you notice any such signs.
What are the causes of Gout?
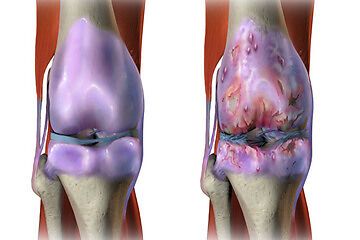
Gout occurs when urate crystals accumulate in your joint, causing the inflammation and intense pain of a gout attack. Urate crystals can form when you have high levels of uric acid in your blood. Your body produces uric acid when it breaks down purines — substances that are found naturally in your body.
Purines are also found in certain foods, including red meat and organ meats, such as liver. Purine-rich seafood includes anchovies, sardines, mussels, scallops, trout and tuna. Alcoholic beverages, especially beer, and drinks sweetened with fruit sugar (fructose) promote higher levels of uric acid.
Certain chronic conditions also may increase your risk of Gout, including diabetes and heart disease.
Diagnosis of Gout
To diagnose gout, your doctor will review your personal and family medical history, perform a thorough physical evaluation.
Some tests that are normally done are as:
- X-ray imaging. Joint X-rays can be helpful to rule out other causes of joint inflammation.
- Joint fluid test. Your doctor may use a needle to draw fluid from your affected joint. Urate crystals may be visible when the fluid is examined under a microscope.
What are the complications of Gout?
A few of the comorbidities you may face with Gout are:
- Left untreated, People with gout can develop more-severe conditions, such as: Recurrent gout , Advanced gout , Kidney Stones .Tell your doctor if your signs and symptoms aren't improving despite treatment for Gout.
Prevention of Gout
Preventing and treating illnesses that can become the risk factor for gout is the best way to curb out it's complications. Make sure to change a few of your lifestyle habits and do regular physical exercise (not intense one). Talk to your doctor and take the help of a dietician who can suggest a decent diet to avert gout. A diet is a healthy component of Gout treatment in Ayurveda!