What is Proteinuria?

Most people notice bubbles in the urine when they pee right after getting up in the morning. Sometimes discerning frothy urine can be a sign of overproduction of proteins by the body, but in most cases, it signifies some renal disorder. People with proteinuria may have more than enough amount of protein in the urine, which makes the urine look like a scrambled egg.
Not healthy kidneys may allow you to vent such an amount unless some extreme conditions enable them to do so. However, the right approach to treating proteinuria such as proteinuria ayurvedic treatment can help avert the progression of this condition into the late stages of CKD.
Various Protein’s which is associated with proteinuria?
There are various proteins present in our blood for the well-being, but the two primary forms are known to be albumin and globulins. Albumin is abundantly found in the blood, accounting for nearly 50% of the total serum proteins. Its role is not limited to keeping the muscles healthy as like other protein; in fact, they help the body with other regulatory functions. These may include:
- Keeping the right balance of fluid and electrolyte in the circulatory system
- Acting as a transporting agent
- Preventing the body from getting swelled
The less albumin in your urine, the better it is for you
Why is the measurement of urine albumin important?
Measurement of urine albumin is an essential factor to know:
- If you have kidney disease
- To monitor the progression of any kidney disease
Health care providers usually conduct proteinuria as a part of their routine to understand a patient’s kidney function. A urine albumin level that stays the same or lowers down for a couple of tests means that the treatment is working. The treatment to lower urine albumin may lower the risk of developing into the late stages of kidney disease.
Talk with your healthcare provider about how often you should get it tested.
What are the causes of Proteinuria?
The different causes attached to the occurrence of proteinuria are:
- Diseases related to the filters of the kidneys; for instance Glomerulonephritis
- Urine infection also prompts proteinuria, but there are other signs to check such as urinary tract infections
- Eclampsia is the sign of proteinuria in a pregnant woman
- Proteinuria can be a sign of some other conditions and diseases such as congestive heart failure
- Temporary proteinuria may also occur when you do much of physical exercise or if you have a high fever
- Sometimes, proteinuria can be observed in the day, but not in the morning (called orthostatic proteinuria)
- Sometimes dehydration also causes the urine to become foamy with protein in it
- High blood sugar level when not controlled for a long time can also result in the damage to the filters of the kidneys
Overconsumption of protein may also result in protein leakage when the kidney function is a bit low.
Are there any symptoms of proteinuria?
- Usually, there are no symptoms of proteinuria, but if the protein leakage is extreme, you may notice the frothy appearance of the urine.
- On account of albumin leakage, you may also face the problems related to swelling, in which there is excess water deposited in the cells and tissues.
Apart, shortness of breath, needing to urinate more often, dry and itchy skin, fatigue, vomiting, nausea, hiccups are some of the subtle signs that are also observed in the people having proteinuria.
Are there any specific types of proteinuria?
Transient proteinuria is the protein leakage arising because of changes in physical health. But, this type of proteinuria is not considered as a measurement of kidney disease as it goes away when you return to your normal health.
Orthostatic proteinuria involves more urine when standing in an upright position. Such type of proteinuria can be seen in thin and tall adolescents. Even in this type of proteinuria, there is no manifestation leading to kidney disease.
Persistent proteinuria is another type of proteinuria indicating a diseased kidney, such as Glomerulonephritis and primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS). Microalbuminuria is a low level of albumin in the urine because of some conditions like diabetes and hypertension, which can progress to end-stage renal disease.
How is proteinuria detected?
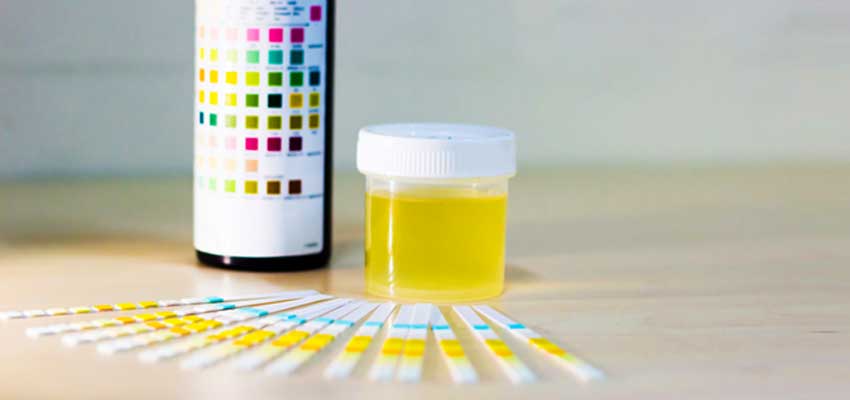
A healthcare provider usually tests for proteinuria using a dipstick test along with urine albumin and serum creatinine. You will be told to collect a urine sample in a container that is tested by the lab physician.
Dipstick for albumin: A dipstick test can detect the presence of albumin in the urine. A dipstick is a chemical strip of paper placed in the urine. If the strip changes its color, then it means your urine has albumin present in the urine.
Urine albumin and creatinine ratio: The purpose of the urine albumin and creatinine ratio is to know if you have kidney problems. The test measures albumin in response to the creatinine in the urine. If the UACR for the patient is estimated more than 30 mg/g, it indicates impaired kidney function.
How often should you go for a proteinuria test?
People who are at a high risk of kidney disease should add these test as a part of their routine checkups. Those who have increased risk of proteinuria include:
- Having diabetes
- High levels of high blood pressure
- Having kidney diseases running in their families
- If you are older than 65
If you have proteinuria, does it mean your kidney is falling ill?
Having albumin in the urine is a sign of kidney disease, but your doctor will conduct it twice or thrice to know the exact cause. Sometimes, proteinuria is temporarily caused by not drinking enough water for a couple of days. If your doctor suspects you have kidney disease, there are some other tests he will do to know how well your kidneys are working.
These may include:
- Glomerular filtration rate: This is the kind of blood test; a doctor does to know how well your kidneys are performing.
- A kidney biopsy: A kidney biopsy can help to know the cause of kidney problems and the percentage of your damaged kidneys.
- Imaging tests: An ultrasound of the kidney and the urinary tract to produce their pictures for kidney stones.
- Urinalysis: A urine analysis to know if your urine has RBCs
Contact your doctor and get the required tests, if needed!